Grantee Research Project Results
Final Report: Long Term Metabolic Consequences of Exposures to Multipollutant Atmospheres in the Great Lakes Region
EPA Grant Number: R834797C003Subproject: this is subproject number 003 , established and managed by the Center Director under grant R834797
(EPA does not fund or establish subprojects; EPA awards and manages the overall grant for this center).
Center: Center for Research on Early Childhood Exposure and Development in Puerto Rico
Center Director: Alshawabkeh, Akram
Title: Long Term Metabolic Consequences of Exposures to Multipollutant Atmospheres in the Great Lakes Region
Investigators: Rajagopalan, Sanjay , Sun, Qinghua
Institution: The Ohio State University
EPA Project Officer: Chung, Serena
Project Period: December 1, 2010 through November 30, 2015 (Extended to December 31, 2016)
RFA: Clean Air Research Centers (2009) RFA Text | Recipients Lists
Research Category: Human Health , Air
Objective:
We have recently demonstrated that short-term exposure to inhaled concentrated airborne particulate (CAP) matter <2.5μm (PM2.5) results in components of cardiometabolic syndrome (CMS) including development of hypertension and insulin resistance. In this project, we had hypothesized that chronic inhalation of CAP in conjunction with gaseous components such as ozone from distinct multipollutant atmospheres synergistically interacts with diet and genetic susceptibility to influence development of CMS. Project 3 has been an integral component of the overarching theme of this center that primary air pollutants, fine PM (PM2.5) and ozone (O3), cause cardiometabolic health effects that are dependent on the local atmospheric multipollutant milieu, predisposing factors, and the interactive toxicity of multipollutant coexposure. The experiments proposed were natural extensions of human research outlined in Project 1 and acute experiments in Project 2 and focused on conducting chronic inhalation toxicology studies in diet fed and genetic models of obesity/diabetes. In Aim 1, simultaneous chronic exposure to multipollutant CAP from two locations in Columbus, OH representing near-roadside/traffic or remotely transported/aged emissions were examined in combination with high fat chow (HFC). The impact of CAP on glucose/insulin homeostasis, adipokines, insulin signaling, adipose and pulmonary inflammation and an analysis of dose dependence and CAP components were evaluated in diet sensitive (C57BL/6) and genetic models of Type II diabetes susceptibility (KKA/y). In Aim 2, we investigated the effect of co-exposure of multipollutant CAP with ozone on the temporal development of insulin resistance and adipose/lung inflammation using the KKA/y model. We will assess dose response relationship of multipollutant-O3 mixture on insulin resistance measures (HOMA-IR and IPGTT) and novel mediators of innate immune, pivotal to the development of metabolic derangement. Based on data from Aims 1 and 2, we designed experiments in Aim 3, which helped us assess chronic effects of multipollutant CAP in potentiating inflammatory monocyte activation and infiltration into tissue niches as a central mechanism for mediating adverse metabolic effects of CAP. Using state of the art multiple exposure systems available at OSU (OASIS-1 and OASIS-2) and MSU in conjunction the resources available at the ECC including the use of several novel and novel high-time resolution exposure characterization methods, we were able to elucidate and improved our understanding of the metabolic effects of PM2.5 alone and in conjunction with ozone.
Summary/Accomplishments (Outputs/Outcomes):
| Duration | Models | Exposures | Main Findings | |
| 10 wks | C57BL/6 mice | *PM2.5 (75 μg/m3) | PM2.5 exposure induces both oxidative stress and ER stress in mouse lung and liver tissues through PERK/eIF2α/ATF6/IRE1α-mediated UPR pathway | 2010 1 |
| 10 wks | C57BL/6 & p47-/- mice on HFD/NCD | *PM2.5 (111 μg/m3) | PM2.5 increases fat content, macrophage infiltration in adipose tissue and vascular function in young mice. P47 (phox) deficiency improves IR in response to PM2.5. | 2010 2 |
| 10 mths | C57BL/6 mice | *PM2.5 (94 μg/m3) | PM2.5 induces IR in adipose tissue, liver and skeletal muscle possibly through increased cytokine, mitochondrial alteration, oxidation and decreased Akt. | 2011 3 |
| 2 mths | ApoE -/- mice | *PM2.5 (97 μg/m3) | PM2.5 results in increased superoxide production and | 2011 4 |
| | | | decrease of mitochondrial number/UCP1 expression in BAT. WAT/BAT-specific genes are also abnormal. | |
| 3/10 wks | C57BL/6 mice | *PM2.5 (77 μg/m3) | PM2.5 induces a NASH-like phenotype and impairs hepatic glucose metabolism | 2013 5 |
| 17 wks | C57/CCR2-/- HFD | *PM2.5(117 μg/m3) | PM2.5 increases IR and hepatic lipids. CCR2-/- partially rescued the effect of PM2.5. | 2013 6 |
| 10 mths | C57BL/6 mice | *PM2.5 (94 μg/m3) | PM2.5 induces macrophage infiltration, unfolded protein response, lipid deposition | 2013 7 |
| 8 weeks | Sprague Dawley | PM2.5 + Ozone | PM2.5 +O3 resulted in increase of macrophage infiltration in both epicardial and perirenal adipose (EAT and PAT) of high-fructose fed rats. Tnf, Mcp-1 were upregulated while IL-10 and adiponectin, were reduced. Decreased mitochondrial area and increased macrophages noted in EAT and PAT. | 20138 |
| 5-8 week | KKAy Mice | *PM2.5 (82 μg/m3) | PM2.5 decreased O2 consumption, CO2 production, respiratory exchange ratio and thermogenesis. Increased inflammation in insulin responsive organs. | 20149 |
| 10 weeks | C57Bl/6 WT or p47phox-/- | *PM2.5 (75 μg/m3) | Exposure to PM2.5 led to activation of the transforming growth factor β-SMAD3 signaling, increased liver collagen, suppression of PPAR gamma signaling | 201510 |
| 18 weeks | LDLR-/- mice | PM2.5 (75 μg/m3) | Exposure to PM2.5 increases 7-ketocholesterol content in LDL/VLDL and increase atherosclerosis. This response is dependent on CD36 mediated uptake of ox- LDL in macrophages. | 201411 |
| 2 weeks | KKAy Mice | 0.5 ppm ozone | CD11b(+)Gr-1(lo)7/4(hi) macrophages increased by 200% in adipose but unchanged in blood. Glucose levels were not different in the insulin tolerance test between air- and ozone-exposed mice, whereas fasting insulin levels and HOMA-IR in ozone-exposed animals were significantly reduced. Increased insulin signaling in skeletal muscle and liver, but not adipose tissues. Ozone caused decrease in body weight and plasma leptin. | 201612 |
| 2 weeks | KK mice | 0.5 ppm ozone | Plasma insulin and leptin levels were reduced in O3- exposed mice. ncreased monocytes/macrophages in both blood and visceral adipose tissue. Inflammatory monocytes/macrophages increased both systemically and locally. Multiple inflammatory genes including CXCL-11, IFN-gamma, TNFalpha, IL-12, and iNOS were up-regulated in visceral adipose tissue. Expression of oxidative stress-related genes such as Cox4, Cox5a, Scd1, Nrf1, and Nrf2, increased in visceral adipose | 201613 |
Conclusions:
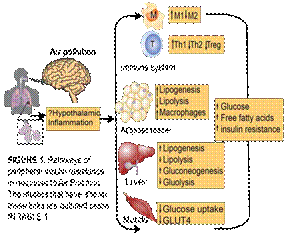
Figure `
Journal Articles on this Report : 34 Displayed | Download in RIS Format
| Other subproject views: | All 45 publications | 34 publications in selected types | All 34 journal articles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Other center views: | All 148 publications | 72 publications in selected types | All 72 journal articles |
| Type | Citation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Blazek A, Rutsky J, Osei K, Maiseyeu A, Rajagopalan S. Exercise-mediated changes in high-density lipoprotein: impact on form and function. American Heart Journal 2013;166(3):392-400. |
R834797 (2013) R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C003 (2013) R834797C003 (2014) R834797C003 (2015) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit |
|
|
Brook RD, Rajagopalan S. Can what you breathe trigger a stroke within hours? Comment on "ambient air pollution and the risk of acute ischemic stroke". Archives of Internal Medicine 2012;172(3):235-236. |
R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C003 (2012) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit |
|
|
Brook RD, Bard RL, Kaplan MJ, Yalavarthi S, Morishita M, Dvonch JT, Wang L, Yang H-Y, Spino C, Mukherjee B, Oral EA, Sun Q, Brook JR, Harkema J, Rajagopalan S. The effect of acute exposure to coarse particulate matter air pollution in a rural location on circulating endothelial progenitor cells: results from a randomized controlled study. Inhalation Toxicology 2013;25(10):587-592. |
R834797 (2013) R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C001 (2013) R834797C001 (2014) R834797C001 (2015) R834797C001 (2016) R834797C001 (Final) R834797C002 (2013) R834797C002 (2014) R834797C002 (2015) R834797C002 (2016) R834797C002 (Final) R834797C003 (2013) R834797C003 (Final) R833740 (2012) R833740 (Final) |
Exit |
|
|
Brook RD, Xu X, Bard RL, Dvonch JT, Morishita M, Kaciroti N, Sun Q, Harkema J, Rajagopalan S. Reduced metabolic insulin sensitivity following sub-acute exposures to low levels of ambient fine particulate matter air pollution. The Science of the Total Environment 2013;448:66-71. |
R834797 (2012) R834797 (2013) R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (Final) R834797C001 (2012) R834797C001 (2013) R834797C001 (2014) R834797C001 (2015) R834797C001 (2016) R834797C001 (Final) R834797C002 (2012) R834797C002 (2013) R834797C002 (2014) R834797C002 (2015) R834797C002 (2016) R834797C002 (Final) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Deiuliis JA, Kampfrath T, Zhong J, Oghumu S, Maiseyeu A, Chen LC, Sun Q, Satoskar AR, Rajagopalan S. Pulmonary T cell activation in response to chronic particulate air pollution. American Journal of Physiology:Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 2012;302(4):L399-L409. |
R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Liu C, Ying Z, Harkema J, Sun Q, Rajagopalan S. Epidemiological and experimental links between air pollution and type 2 diabetes. Toxicologic Pathology 2013;41(2):361-373. |
R834797 (2013) R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C002 (2012) R834797C002 (2013) R834797C002 (2014) R834797C002 (2015) R834797C002 (2016) R834797C002 (Final) R834797C003 (2013) R834797C003 (2014) R834797C003 (2015) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Liu C, Xu X, Bai Y, Wang TY, Rao X, Wang A, Sun L, Ying Z, Gushchina L, Maiseyeu A, Morishita M, Sun Q, Harkema JR, Rajagopalan S. Air pollution-mediated susceptibility to inflammation and insulin resistance:influence of CCR2 pathways in mice. Environmental Health Perspectives 2014;122(1):17-26. |
R834797 (2013) R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C002 (2014) R834797C002 (2015) R834797C002 (2016) R834797C002 (Final) R834797C003 (2014) R834797C003 (2015) R834797C003 (Final) |
|
|
|
Liu C, Bai Y, Xu X, Sun L, Wang A, Wang TY, Maurya SK, Periasamy M, Morishita M, Harkema J, Ying Z, Sun Q, Rajagopalan S. Exaggerated effects of particulate matter air pollution in genetic type II diabetes mellitus. Particle and Fibre Toxicology 2014;11:27. |
R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C002 (2014) R834797C002 (2015) R834797C002 (2016) R834797C002 (Final) R834797C003 (2014) R834797C003 (2015) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Liu C, Fonken LK, Wang A, Maiseyeu A, Bai Y, Wang T-Y, Maurya S, Ko Y-A, Periasamy M, Dvonch T, Morishita M, Brook RD, Harkema J, Ying Z, Mukherjee B, Sun Q, Nelson RJ, Rajagopalan S. Central IKKβ inhibition prevents air pollution mediated peripheral inflammation and exaggeration of type II diabetes. Particle and Fibre Toxicology 2014;11:53. |
R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C003 (2014) R834797C003 (2015) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Mendez R, Zheng Z, Fan Z, Rajagopalan S, Sun Q, Zhang K. Exposure to fine airborne particulate matter induces macrophage infiltration, unfolded protein response, and lipid deposition in white adipose tissue. American Journal of Translational Research 2013;5(2):224-234. |
R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C003 (2014) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Morishita M, Bard RL, Kaciroti N, Fitzner CA, Dvonch T, Harkema JR, Rajagopalan S, Brook RD. Exploration of the composition and sources of urban fine particulate matter associated with same-day cardiovascular health effects in Dearborn, Michigan. Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology 2015;25(2):145-152. |
R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C001 (2014) R834797C001 (2015) R834797C001 (2016) R834797C001 (Final) R834797C002 (2014) R834797C002 (2015) R834797C002 (2016) R834797C002 (Final) R834797C003 (2015) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit |
|
|
Morishita M, Bard RL, Wang L, Das R, Dvonch JT, Spino C, Mukherjee B, Sun Q, Harkema JR, Rajagopalan S, Brook RD. The characteristics of coarse particulate matter air pollution associated with alterations in blood pressure and heart rate during controlled exposures. Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology 2015;25(2):153-159. |
R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C001 (2014) R834797C001 (2015) R834797C001 (2016) R834797C001 (Final) R834797C002 (2015) R834797C002 (2016) R834797C002 (Final) R834797C003 (2015) R834797C003 (Final) R833740 (Final) |
Exit Exit |
|
|
Newby DE, Mannucci PM, Tell GS, Baccarelli AA, Brook RD, Donaldson K, Forastiere F, Franchini M, Franco OH, Graham I, Hoek G, Hoffmann B, Hoylaerts MF, Kunzli N, Mills N, Pekkanen J, Peters A, Piepoli MF, Rajagopalan S, Storey RF, ESC Working Group on Thrombosis, European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention and Rehabilitation, ESC Heart Failure Association. Expert position paper on air pollution and cardiovascular disease. European Heart Journal 2015;36(2):83-93b. |
R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C003 (2015) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Rajagopalan S, Brook RD. Personalizing your airspace and your health. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2015;65(21):2288-2290. |
R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C003 (2015) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Rao X, Zhong J, Maiseyeu A, Gopalakrishnan B, Villamena FA, Chen LC, Harkema JR, Sun Q, Rajagopalan S. CD36-dependent 7-ketocholesterol accumulation in macrophages mediates progression of atherosclerosis in response to chronic air pollution exposure. Circulation Research 2014;115(9):770-780. |
R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C002 (2015) R834797C002 (Final) R834797C003 (2014) R834797C003 (2015) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Rao X, Patel P, Puett R, Rajagopalan S. Air pollution as a risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Toxicological Sciences 2015;143(2):231-241. |
R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C003 (2014) R834797C003 (2015) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Rao X, Montresor-Lopez J, Puett R, Rajagopalan S, Brook RD. Ambient air pollution:an emerging risk factor for diabetes mellitus. Current Diabetes Reports 2015;15(6):603. |
R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C003 (2015) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit |
|
|
Sun L, Liu C, Xu X, Ying Z, Maiseyeu A, Wang A, Allen K, Lewandowski RP, Bramble LA, Morishita M, Wagner JG, Dvonch JT, Sun Z, Yan X, Brook RD, Rajagopalan S, Harkema JR, Sun Q, Fan Z. Ambient fine particulate matter and ozone exposures induce inflammation in epicardial and perirenal adipose tissues in rats fed a high fructose diet. Particle and Fibre Toxicology 2013;10:43. |
R834797 (2013) R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (Final) R834797C001 (2013) R834797C002 (2013) R834797C002 (2014) R834797C002 (2015) R834797C002 (Final) R834797C003 (2013) R834797C003 (2014) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Wagner JG, Morishita M, Keeler GJ, Harkema JR. Divergent effects of urban particulate air pollution on allergic airway responses in experimental asthma:a comparison of field exposure studies. Environmental Health 2012;11:45 (13 pp.). |
R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Wagner JG, Allen K, Yang HY, Nan B, Morishita M, Mukherjee B, Dvonch JT, Spino C, Fink GD, Rajagopalan S, Sun Q, Brook RD, Harkema JR. Cardiovascular depression in rats exposed to inhaled particulate matter and ozone: effects of diet-induced metabolic syndrome. Environmental Health Perspectives 2014;122(1):27-33. |
R834797 (2013) R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C001 (2013) R834797C001 (Final) R834797C002 (2013) R834797C002 (2014) R834797C002 (2015) R834797C002 (2016) R834797C002 (Final) R834797C003 (2013) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit |
|
|
Wellenius GA, Boyle LD, Wilker EH, Sorond FA, Coull BA, Koutrakis P, Mittleman MA, Lipsitz LA. Ambient fine particulate matter alters cerebral hemodynamics in the elderly. Stroke 2013;44(6):1532-1536. |
R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C001 (Final) R834797C002 (2016) R834797C003 (Final) R834798 (2013) R834798 (2014) R834798 (Final) R834798C002 (Final) R834798C003 (2013) R834798C003 (2014) R834798C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Wold LE, Ying Z, Hutchinson KR, Velten M, Gorr MW, Velten C, Youtz DJ, Wang A, Lucchesi PA, Sun Q, Rajagopalan S. Cardiovascular remodeling in response to long-term exposure to fine particulate matter air pollution. Circulation:Heart Failure 2012;5(4):452-461. |
R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C003 (2012) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Xu X, Liu C, Xu Z, Tzan K, Wang A, Rajagopalan S, Sun Q. Altered adipocyte progenitor population and adipose-related gene profile in adipose tissue by long-term high-fat diet in mice. Life Sciences 2012;90(25-26):1001-1009. |
R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C003 (2012) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Ying Z, Xu X, Chen M, Liu D, Zhong M, Chen L-C, Sun Q, Rajagopalan S. A synergistic vascular effect of airborne particulate matter and nickel in a mouse model. Toxicological Sciences 2013;135(1):72-80. |
R834797 (2013) R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C003 (2014) R834797C003 (2015) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Ying Z, Xu X, Bai Y, Zhong J, Chen M, Liang Y, Zhao J, Liu D, Morishita M, Sun Q, Spino C, Brook RD, Harkema JR, Rajagopalan S. Long-term exposure to concentrated ambient PM2.5 increases mouse blood pressure through abnormal activation of sympathetic nervous system:a role for hypothalamic inflammation. Environmental Health Perspectives 2014;122(1):79-86. |
R834797 (2013) R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C002 (2013) R834797C002 (2014) R834797C002 (2015) R834797C002 (2016) R834797C002 (Final) R834797C003 (2013) R834797C003 (2014) R834797C003 (2015) R834797C003 (Final) |
|
|
|
Ying Z, Xie X, Bai Y, Chen M, Wang X, Zhang X, Morishita M, Sun Q, Rajagopalan S. Exposure to concentrated ambient particulate matter induces reversible increase of heart weight in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Particle and Fibre Toxicology 2015;12:15 (10 pp.). |
R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C003 (2015) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit |
|
|
Zheng Z, Xu X, Zhang X, Wang A, Zhang C, Huttemann M, Grossman LI, Chen LC, Rajagopalan S, Sun Q, Zhang K. Exposure to ambient particulate matter induces a NASH-like phenotype and impairs hepatic glucose metabolism in an animal model. Journal of Hepatology 2013;58(1):148-154. |
R834797 (2014) R834797 (2015) R834797 (2016) R834797 (Final) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Zhong J, Allen K, Rao X, Ying Z, Braunstein Z, Kankanala SR, Xia C, Wang X, Bramble LA, Wagner JG, Lewandowski R, Sun Q, Harkema JR, Rajagopalan S. (2016) Repeated ozone exposure exacerbates insulin resistance and activates innate immune response in genetically susceptible mice. Inhalation Toxicology 2016;28(9):383-392. |
R834797 (Final) R834797C003 (Final) |
Exit |
|
|
Rajagopalan S, Brook RD. (2012) Air Pollution and Type II Diabetes:Mechanistic Insights Diabetes. 2012 Dec;61(12):3037-45. PMCID:PMC3501850. |
R834797C003 (Final) |
not available |
|
|
Xu X, Rao X, Wang TY, Jiang SY, Ying Z, Liu C, Wang A, Zhong M, Deiuliis JA, Maiseyeu A, Rajagopalan S, Lippmann M, Chen LC, Sun Q. (2012) Effect of co-exposure to nickel and particulate matter on insulin resistance and mitochondrial dysfunction in a mouse model. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2012 Nov 5;9:40. PMCID:PMC3545913. |
R834797C003 (Final) |
not available |
|
|
Münzel T, Sørensen M, Gori T, Schmidt FP, Rao X, Brook FR, Chen LC, Brook RD, Rajagopalan S. (2016) Environmental stressors and cardio-metabolic disease:part II-mechanistic insights.Eur Heart J. 2016 Jul 26. pii:ehw294. [Epub ahead of print] PMID:27460891. |
R834797C003 (Final) |
not available |
|
|
Ying Z, Allen K, Zhong J, Chen M, Williams KM, Wagner JG, Lewandowski R, Sun Q, Rajagopalan S, Harkema JR. (2016) Subacute inhalation exposure to ozone induces systemic inflammation but not insulin resistance in a diabetic mouse model. Inhal Toxicol. 2016;28(4):155-63. PMCID:PMC4836866. |
R834797C003 (Final) |
not available |
|
|
Subacute inhalation exposure to ozone induces systemic inflammation but not insulin resistance in a diabetic mouse model. Ying Z, Allen K, Zhong J, Chen M, Williams KM, Wagner JG, Lewandowski R, Sun Q, Rajagopalan S, Harkema JR. Inhal Toxicol. 2016;28(4):155-63. |
R834797C003 (2016) R834797C003 (Final) |
not available |
|
|
Repeated ozone exposure exacerbates insulin resistance and activates innate immune response in genetically susceptible mice. Zhong J, Allen K, Rao X, Ying Z, Braunstein Z, Kankanala SR, Xia C, Wang X, Bramble LA, Wagner JG, Lewandowski R, Sun Q, Harkema JR, Rajagopalan S. Inhal Toxicol. 2016 Aug;28(9):383-92. |
R834797C003 (2016) R834797C003 (Final) |
not available |
Supplemental Keywords:
Air, Scientific Discipline, ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT, Health Risk Assessment, Biology, Biochemistry, air toxics, Risk Assessment, aerosol particles, physiology, human exposure, particulate matter, cardiotoxicity, susceptible populations, ambient air quality, cardiopulmonary, acute cardiovascualr effectsProgress and Final Reports:
Original AbstractMain Center Abstract and Reports:
R834797 Center for Research on Early Childhood Exposure and Development in Puerto Rico Subprojects under this Center: (EPA does not fund or establish subprojects; EPA awards and manages the overall grant for this center).
R834797C001 Cardiometabolic Effects of Exposure to Differing Mixtures and Concentrations of PM2.5 in Obese and Lean Adults
R834797C002 Cardiometabolic, Autonomic, and Airway Toxicity of Acute Exposures to PM2.5 from Multipollutant Atmospheres in the Great Lakes Region
R834797C003 Long Term Metabolic Consequences of Exposures to Multipollutant Atmospheres in the Great Lakes Region
The perspectives, information and conclusions conveyed in research project abstracts, progress reports, final reports, journal abstracts and journal publications convey the viewpoints of the principal investigator and may not represent the views and policies of ORD and EPA. Conclusions drawn by the principal investigators have not been reviewed by the Agency.
Project Research Results
- 2016 Progress Report
- 2015 Progress Report
- 2014 Progress Report
- 2013 Progress Report
- 2012 Progress Report
- 2011 Progress Report
- Original Abstract
34 journal articles for this subproject
Main Center: R834797
148 publications for this center
72 journal articles for this center
