Grantee Research Project Results
2014 Progress Report: Project B: Exposure Project: Mn, DDT/E and PBDE Exposure to Farmworker Children
EPA Grant Number: R834513C002Subproject: this is subproject number 002 , established and managed by the Center Director under grant R834513
(EPA does not fund or establish subprojects; EPA awards and manages the overall grant for this center).
Center: Center for Research on Early Childhood Exposure and Development in Puerto Rico
Center Director: Alshawabkeh, Akram
Title: Project B: Exposure Project: Mn, DDT/E and PBDE Exposure to Farmworker Children
Investigators: Eskenazi, Brenda , Bradman, Asa , Jerrett, Michael , Molitor, John , Holland, Nina T. , Harley, Kim , Sjodin, Andreas , Smith, Donald , Arora, Manish
Current Investigators: Eskenazi, Brenda , Harley, Kim , Holland, Nina T. , Jerrett, Michael , Sjodin, Andreas , Arora, Manish , Smith, Donald , Eisen, Ellen , Molitor, John , Hubbard, Alan , Lustig, Robert
Institution: University of California - Berkeley , University of California - Santa Cruz , Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Current Institution: University of California - Berkeley
EPA Project Officer: Hahn, Intaek
Project Period: August 1, 2009 through July 31, 2014 (Extended to July 31, 2017)
Project Period Covered by this Report: August 1, 2009 through July 31,2014
RFA: Children's Environmental Health and Disease Prevention Research Centers (with NIEHS) (2009) RFA Text | Recipients Lists
Research Category: Children's Health , Human Health
Objective:
In Project B, we are studying novel methods of examining prenatal exposure to Mn, PBDE, and DDT/E compounds. For exposure to Mn, we are measuring Mn levels in shed deciduous teeth and in hair collected when the children were 10.5 years of age. For PBDEs and DDT/E, we are developing models to back-extrapolate prenatal exposure levels from 9-year measured levels and other determinants of exposure.
Progress Summary:
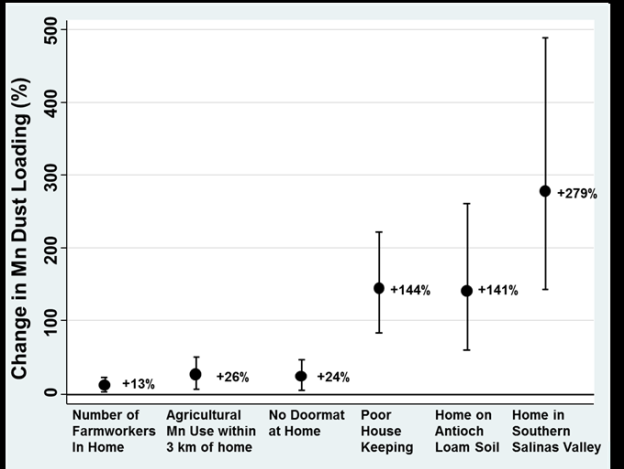
| Children with Tooth Mn Levels | Children with Tooth and Dust Mn Levels | |||||
| Predictor Variable | % Changeb (95% CI) | p-value | Partial r2 (%) | % Changeb (95% CI) | p-value | Partial r2 (%) |
| Maternal farmwork | 10.1 (0.1, 21.3) | 0.05 | 1.8 | 15.8 (1.9, 31.6) | 0.03 | 3.9 |
| (Prenatal yes vs. no) | ||||||
| Farmworker shoes in | ||||||
| home | 8.1 (4.3, 12.0) | <0.001 | 8.4 | 6.4 (1.5, 11.4) | 0.01 | 5.2 |
| (Prenatal per worker) | ||||||
| Agricultural fungicide | ||||||
| use prenatal within 3 | ||||||
| km (per IQRc = 809 kg ) | 4.9 (0.9, 9.1) | 0.02 | 2.8 | 3.4 (-1.6, 8.6) | 0.19 | 1.4 |
| Soil type | 15.1 (4.6, 26.6) | 0.004 | 4.0 | 20.7 (6.3, 37.1) | 0.004 | 6.4 |
| (Antioch Loam vs. | ||||||
| other) | ||||||
| Mother smoked | -33.8 (-46.6, -18.0) | <0.001 | 6.7 | -40.3 (-55.3, -20.2) | 0.001 | 9.0 |
| (Prenatal yes vs. no) | ||||||
| Mn dust loading (per IQRc = 1465 µg/m2) | - | - | 3.3 (0.3, 6.4) | 0.03 | 3.6 | |
| R2 for Model | 22% | 29% | ||||
- DAPs in child urine: A manuscript examining changes in pesticide excretion during organic food intake is in submission.
- BPA: An article on determinants of BPA exposure in pregnant women was accepted by Environment International (Quiros-Alcala, et al., 2014).
- Within and between subject variability: Dr. Bradman, et al., published a paper in Environmental Health Perspectives examining within and between subject variability in organophosphate metabolite excretion in young children.
- Environmental Quality in Child Care: Dr. Bradman published two studies examining environmental quality in child care, one focusing on flame retardants and one on phthalates.
- Organophosphate levels and PON1 in blood: Dr. Karen Huen (former graduate student with us) published a study reporting on chlorpyrifos and diazinon levels in maternal and infant blood and PON1 status.
- Dietary transitions in a Neanderthal infant: Dr. Manish Arora with Drs. Eskenazi and Bradman and other scientists, published a paper in Nature showing breast feeding transitions in a Neanderthal infant. The study used teeth and data from the CHAMACOS cohort to validate the method applied to a fossil Neanderthal tooth.
Future Activities:
In the next year, we will complete analyses of correlates of PBDE and DDT/E exposure. We expect to publish at least three manuscripts this year, one examining the interrelationships of Mn in biological samples (in review by co-authors), one on the best methods to back-estimate maternal PBDE and DDT/E levels in adult women (near completion), and another on correlates of PBDEs and DDT/E in 9-year old boys. Future analyses also will utilize hierarchical models to evaluate the relationship between predictors of exposure and prenatal and postnatal Mn levels in deciduous teeth.
Journal Articles on this Report : 18 Displayed | Download in RIS Format
| Other subproject views: | All 108 publications | 43 publications in selected types | All 42 journal articles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Other center views: | All 697 publications | 170 publications in selected types | All 169 journal articles |
| Type | Citation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Bradman A, Castorina R, Gaspar F, Nishioka M, Colon M, Weathers W, Egeghy PP, Maddalena R, Williams J, Jenkins PL, McKone TE. Flame retardant exposures in California early childhood education environments. Chemosphere 2014;116:61-66. |
R834513 (2014) R834513C002 (2014) R834513C003 (Final) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Bradman A, Quiros-Alcala L, Castorina R, Schall RA, Camacho J, Holland NT, Barr DB, Eskenazi B. Effect of organic diet intervention on pesticide exposures in young children living in low-income urban and agricultural communities. Environmental Health Perspectives 2015;123(10):1086-1093. |
R834513 (2014) R834513 (2016) R834513C002 (2014) R834513C002 (2015) R834513C002 (2016) R834513C003 (Final) |
|
|
|
Dannemiller KC, Mendell MJ, Macher JM, Kumagai K, Bradman A, Holland N, Harley K, Eskenazi B, Peccia J. Next-generation DNA sequencing reveals that low fungal diversity in house dust is associated with childhood asthma development. Indoor Air 2014;24(3):236-247. |
R834513 (2014) R834513 (2015) R834513C001 (2015) R834513C002 (2014) |
Exit Exit |
|
|
Engel SM, Bradman A, Wolff MS, Rauh VA, Harley KG, Yang JH, Hoepner LA, Barr DB, Yolton K, Vedar MG, Xu Y, Hornung RW, Wetmur JG, Chen J, Holland NT, Perera FP, Whyatt RM, Lanphear BP, Eskenazi B. Prenatal organophosphorus pesticide exposure and child neurodevelopment at 24 months: an analysis of four birth cohorts. Environmental Health Perspectives 2016;124(6):822-830. |
R834513 (2014) R834513 (2015) R834513C001 (2014) R834513C001 (2015) R834513C002 (2014) |
|
|
|
Eskenazi B, Bradman A, Finkton D, Purwar M, Noble JA, Pang R, Burnham O, Cheikh Ismail L, Farhi F, Barros FC, Lambert A, Papageorghiou AT, Carvalho M, Jaffer YA, Bertino E, Gravett MG, Altman DG, Ohuma EO, Kennedy SH, Bhutta ZA, Villar J, International Fetal and Newborn Growth Consortium for the 21st Century. A rapid questionnaire assessment of environmental exposures to pregnant women in the INTERGROWTH-21st Project. BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology 2013;120(Suppl 2):129-138. |
R834513 (2014) R834513C002 (2014) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Eskenazi B, Quiros-Alcala L, Lipsitt JM, Wu LD, Kruger P, Ntimbane T, Nawn JB, Bornman R, Seto E. mSpray: a mobile phone technology to improve malaria control efforts and monitor human exposure to malaria control pesticides in Limpopo, South Africa. Environment International 2014;68:219-226. |
R834513 (2014) R834513C002 (2014) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Gaspar FW, Castorina R, Maddalena RL, Nishioka MG, McKone TE, Bradman A. Phthalate exposure and risk assessment in California child care facilities. Environmental Science & Technology 2014;48(13):7593-7601. |
R834513 (2014) R834513C002 (2014) R834513C002 (2015) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Gunier RB, Bradman A, Jerrett M, Smith DR, Harley KG, Austin C, Vedar M, Arora M, Eskenazi B. Determinants of manganese in prenatal dentin of shed teeth from CHAMACOS children living in an agricultural community. Environmental Science & Technology 2013;47(19):11249-11257. |
R834513 (2013) R834513 (2014) R834513 (Final) R834513C002 (2013) R834513C002 (2014) R826709 (2002) |
Exit Exit |
|
|
Gunier RB, Mora AM, Smith D, Arora M, Austin C, Eskenazi B, Bradman A. Biomarkers of manganese exposure in pregnant women and children living in an agricultural community in California. Environmental Science & Technology 2014;48(24):14695-14702. |
R834513 (2011) R834513 (2013) R834513 (2014) R834513 (2015) R834513 (Final) R834513C002 (2014) R834513C002 (2015) R834513C004 (2011) R826709 (2002) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Gunier RB, Jerrett M, Smith DR, Jursa T, Yousefi P, Camacho J, Hubbard A, Eskenazi B, Bradman A. Determinants of manganese levels in house dust samples from the CHAMACOS cohort. Science of the Total Environment 2014;497-498:360-368. |
R834513 (2012) R834513 (2013) R834513 (2014) R834513 (2015) R834513 (Final) R834513C002 (2010) R834513C002 (2012) R834513C002 (2014) R834513C002 (2015) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Gunier RB, Arora M, Jerrett M, Bradman A, Harley KG, Mora AM, Kogut K, Hubbard A, Austin C, Holland N, Eskenazi B. Manganese in teeth and neurodevelopment in young Mexican-American children. Environmental Research 2015;142:688-695. |
R834513 (2014) R834513 (2015) R834513 (2016) R834513C001 (2014) R834513C001 (2015) R834513C001 (2016) R834513C002 (2014) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Harley KG, Engel SM, Vedar MG, Eskenazi B, Whyatt RM, Lanphear BP, Bradman A, Rauh VA, Yolton K, Hornung RW, Wetmur JG, Chen J, Holland NT, Barr DB, Perera FP, Wolff MS. Prenatal exposure to organophosphate pesticides and fetal growth: pooled results from four longitudinal birth cohort studies. Environmental Health Perspectives 2016;124(7):1084-1092. |
R834513 (2014) R834513 (2015) R834513 (2016) R834513 (Final) R834513C001 (2014) R834513C002 (2014) R834513C002 (Final) R834513C003 (Final) |
|
|
|
Mora AM, van Wendel de Joode B, Mergler D, Cordoba L, Cano C, Quesada R, Smith DR, Menezes-Filho JA, Lundh T, Lindh CH, Bradman A, Eskenazi B. Blood and hair manganese concentrations in pregnant women from the Infants’ Environmental Health Study (ISA) in Costa Rica. Environmental Science & Technology 2014;48(6):3467-3476. |
R834513 (2014) R834513C001 (2014) R834513C002 (2014) R834513C002 (2015) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Quiros-Alcala L, Eskenazi B, Bradman A, Ye X, Calafat AM, Harley K. Determinants of urinary bisphenol A concentrations in Mexican/Mexican-American pregnant women. Environment International 2013;59:152-160. |
R834513 (2013) R834513 (2014) R834513 (Final) R834513C002 (2013) R834513C002 (2014) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Salvatore AL, Castorina R, Camacho J, Morga N, Lopez J, Nishioka M, Barr DB, Eskenazi B, Bradman A. Home-based community health worker intervention to reduce pesticide exposures to farmworkers’ children: a randomized-controlled trial. Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology 2015;25(6):608-615. |
R834513 (2014) R834513 (2015) R834513 (2016) R834513C002 (2014) R834513C002 (2015) R834513C002 (2016) R834513C004 (2015) |
Exit |
|
|
van Wendel de Joode B, Mora AM, Cordoba L, Cano JC, Quesada R, Faniband M, Wesseling C, Ruepert C, Oberg M, Eskenazi B, Mergler D, Lindh CH. Aerial application of mancozeb and urinary ethylene thiourea (ETU) concentrations among pregnant women in Costa Rica: the Infants’ Environmental Health Study (ISA). Environmental Health Perspectives 2014;122(12):1321-1328. |
R834513 (2014) R834513C002 (2014) R834513C002 (2015) |
|
|
|
Verner M-A, Gaspar FW, Chevrier J, Gunier RB, Sjodin A, Bradman A, Eskenazi B. Increasing sample size in prospective birth cohorts:back-extrapolating prenatal levels of persistent organic pollutants in newly enrolled children. Environmental Science & Technology 2015;49(6):3940-3948. |
R834513 (2014) R834513 (2015) R834513C001 (2015) R834513C002 (2014) R834513C002 (2015) |
Exit Exit Exit |
|
|
Warner M, Mocarelli P, Brambilla P, Wesselink A, Patterson Jr. DG, Turner WE, Eskenazi B. Serum TCDD and TEQ concentrations among Seveso women, 20 years after the explosion. Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology 2014;24(6):588-594. |
R834513 (2014) R834513C002 (2014) |
Exit Exit |
Supplemental Keywords:
DDT, DDE, PBDEs, flame retardants, manganese, maneb, mancozeb, pesticides, exposure assessment, biomonitoring, house dust, dust loading, teeth, blood, urine measurements, farmworker, Health, RFA, Scientific Discipline, INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION, Health Risk Assessment, Environmental Policy, Biology, Children's Health, biological markers, harmful environmental agents, pesticide exposure, agricultural community, flame retardants, neurochemical effects, PBDE, children's vulnerablity, farmworkersRelevant Websites:
Center for Environmental Research and Children's Health (CERCH) Exit
Progress and Final Reports:
Original AbstractMain Center Abstract and Reports:
R834513 Center for Research on Early Childhood Exposure and Development in Puerto Rico Subprojects under this Center: (EPA does not fund or establish subprojects; EPA awards and manages the overall grant for this center).
R834513C001 CHAMACOS Cohort Project: Pesticides and PBDE on Neurobehavior and Puberty
R834513C002 Project B: Exposure Project: Mn, DDT/E and PBDE Exposure to Farmworker Children
R834513C003 Epigenetics Project
R834513C004 Community Outreach and Translation Core
The perspectives, information and conclusions conveyed in research project abstracts, progress reports, final reports, journal abstracts and journal publications convey the viewpoints of the principal investigator and may not represent the views and policies of ORD and EPA. Conclusions drawn by the principal investigators have not been reviewed by the Agency.
Project Research Results
- Final Report
- 2016 Progress Report
- 2015 Progress Report
- 2013 Progress Report
- 2012 Progress Report
- 2011 Progress Report
- 2010 Progress Report
- Original Abstract
42 journal articles for this subproject
Main Center: R834513
697 publications for this center
169 journal articles for this center
