Grantee Research Project Results
2008 Progress Report: Nanostructured Materials for Environmental Decontamination of Chlorinated Compounds
EPA Grant Number: GR832374Title: Nanostructured Materials for Environmental Decontamination of Chlorinated Compounds
Investigators: Lu, Yunfeng , John, Vijay T.
Institution: Tulane University
EPA Project Officer: Hahn, Intaek
Project Period: August 1, 2005 through July 31, 2008 (Extended to July 31, 2009)
Project Period Covered by this Report: August 1, 2007 through July 31,2008
Project Amount: $320,000
RFA: Greater Research Opportunities: Research in Nanoscale Science Engineering and Technology (2004) RFA Text | Recipients Lists
Research Category: Hazardous Waste/Remediation , Nanotechnology , Safer Chemicals
Objective:
Progress Summary:
The widespread occurrence of dense non-aqueous phase liquids (DNAPLs) such as the chlorinated hydrocarbons in groundwater and in soil is of serious environmental concern. These contaminants transport rapidly in the subsurface to create a contaminant plume as a result of vertical migration due to their higher density than water. In recent years, the use of zero-valent iron nanoparticles has represented a promising and innovative approach to the destruction of these compounds. But iron nanoparticles aggregate and it is very difficult to deliver these nanoparticles to the site of decontamination.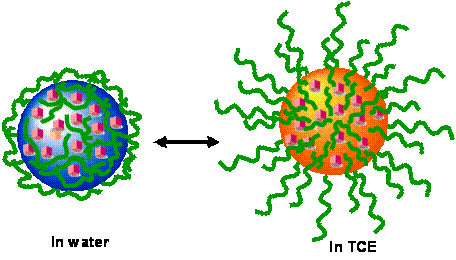
Journal Articles on this Report : 3 Displayed | Download in RIS Format
| Other project views: | All 26 publications | 7 publications in selected types | All 5 journal articles |
|---|
| Type | Citation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Zhan J, Zheng T, Piringer G, Day C, McPherson GL, Lu Y, Papadopoulos K, John VT. Transport characteristics of nanoscale functional zerovalent iron/silica composites for in situ remediation of trichloroethylene. Environmental Science & Technology 2008;42(23):8871-8876. |
GR832374 (2008) GR832374 (Final) |
Exit |
|
|
Zheng T, Pang J, Tan G, He J, McPherson GL, Lu Y, John VT, Zhan J. Surfactant templating effects on the encapsulation of iron oxide nanoparticles within silica microspheres. Langmuir 2007;23(9):5143-5147. |
GR832374 (2006) GR832374 (2008) GR832374 (Final) |
Exit |
|
|
Zheng T, Zhan J, He J, Day C, Lu Y, McPherson GL, Piringer G, John VT. Reactivity characteristics of nanoscale zerovalent iron–silica composites for trichloroethylene remediation. Environmental Science & Technology 2008;42(12):4494-4499. |
GR832374 (2008) GR832374 (Final) |
Exit |
Supplemental Keywords:
Sustainable Industry/Business, RFA, Scientific Discipline, Ecosystem Protection/Environmental Exposure & Risk, TREATMENT/CONTROL, Waste, Water, Remediation, Restoration, Technology for Sustainable Environment, Aquatic Ecosystem Restoration, Sustainable Environment, Environmental Chemistry, Engineering, Chemistry, & Physics, Analytical Chemistry, New/Innovative technologies, Environmental Engineering, Technology, catalysts, reductive dechlorination, pollution prevention, aquifer remediation design, zero valent iron nanoparticles, innovative technologies, environmental sustainability, contaminated aquifers, groundwater contamination, remediation technologies, environmentally applicable nanoparticles, hazardous organics, groundwater remediation, nanotechnology, groundwater, in situ remediation, degradation rates, DNAPL, reductive detoxification, groundwater pollution, reductive degradation of hazardous organicsProgress and Final Reports:
Original AbstractThe perspectives, information and conclusions conveyed in research project abstracts, progress reports, final reports, journal abstracts and journal publications convey the viewpoints of the principal investigator and may not represent the views and policies of ORD and EPA. Conclusions drawn by the principal investigators have not been reviewed by the Agency.
